Geriatric Orthopaedic :
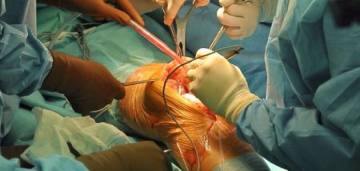
The Special focus section in this issue highlights the difficulty and complexity in treating orthopaedic trauma in elderly patients. Although people are living longer than ever before, few make it to senior status without comorbidities.
During the disc replacement surgery, a small 3-to-4 centimetre incision is made in the front of your neck to access your cervical spine. For the lower back the incision is given from the front usually. The damaged disc is removed and the impinged nerve is then relieved. The disc prosthesis is then inserted into the disc space using specialized and precise instruments. After the new disc is successfully placed, the incision is closed.Conditions such as osteoporosis, Arthritis require special consideration and individualized treatment after trauma.
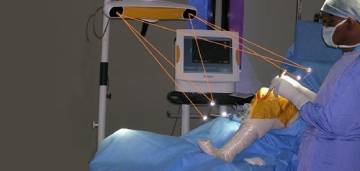
Although a loss in quality of life has been noted to occur in elderly patients after these fracture, The last 10 years has seen improvements in techniques, fixations, and implant design, allowing more patients an early return to function with fewer complications
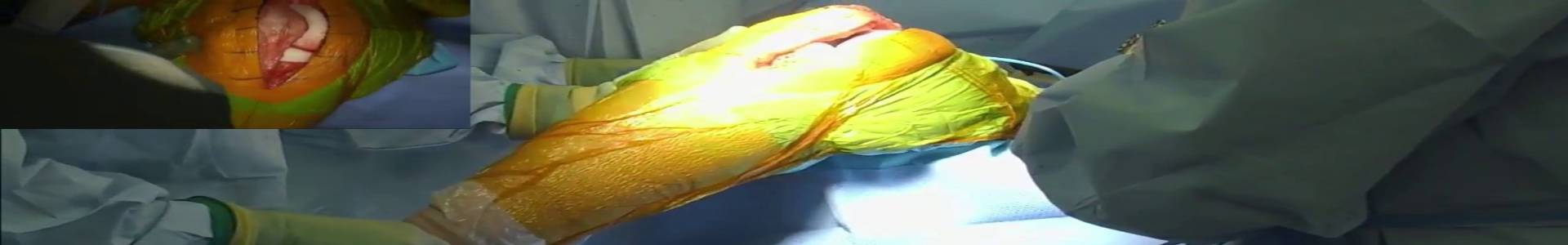
The ideal treatment of these fractures in this population remains controversial, with outcomes studies supporting both non operative and operative treatment. As there are currently no clear guidelines on how to best treat these fracture, present the recent literature on tibial plateau fracture in patients with osteopenic bone.
They stress that management of these fractures must individualized to the patient and injury, and treatment can range from non- operative with early mobilization for low –energy injuries to open reduction and internal fixation or arthroplasty for higher –energy injuries or for patients with higher demands.