In the realm of knee injuries, a torn meniscus is a common occurrence that can cause significant discomfort and hinder daily activities. Whether you’re an athlete or simply going about your daily routine, understanding the symptoms of a torn meniscus is crucial for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment. In this blog post, we’ll delve into what a torn meniscus is, its symptoms, causes, and available treatment options.

What is a Torn Meniscus?
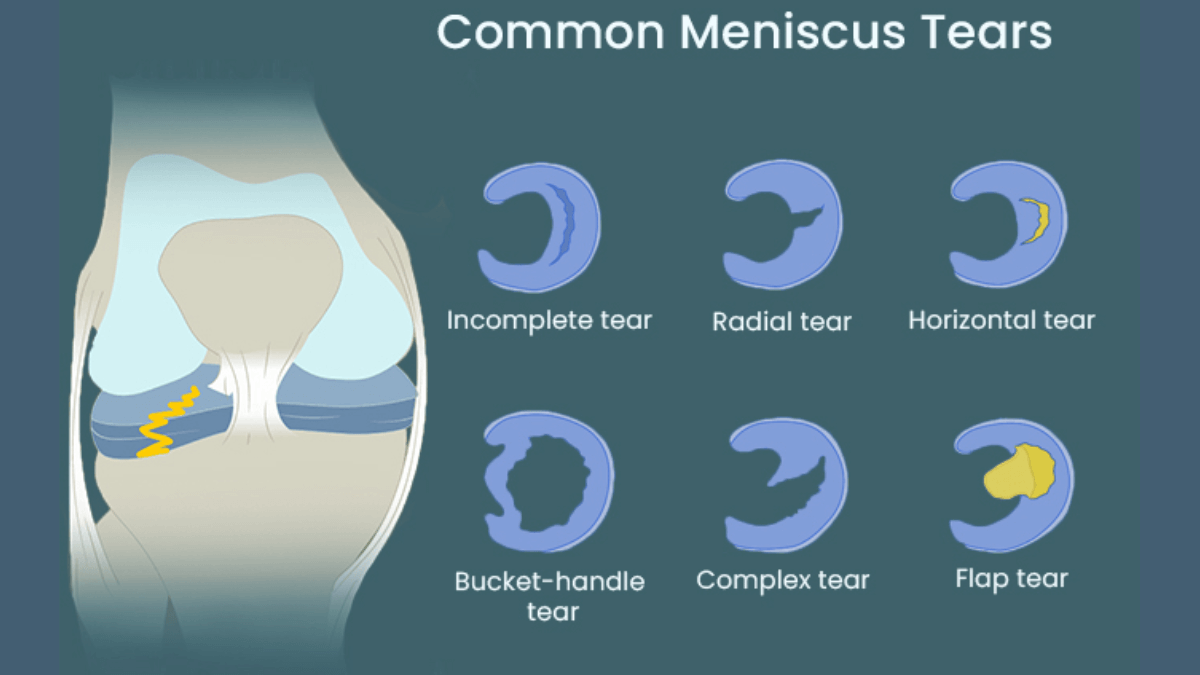
The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage in the knee joint that acts as a cushion and helps distribute weight across the joint. A torn meniscus occurs when this cartilage tears, often due to sudden twisting movements, direct impact, or degenerative changes associated with aging. It’s one of the most common knee injuries, particularly among athletes involved in sports that require pivoting or sudden stops and starts.
Symptoms of a Torn Meniscus
- Pain: Pain, often located on the inner or outer side of the knee, is a primary symptom of a torn meniscus. The severity of pain can vary depending on the extent and location of the tear.
- Swelling: Swelling around the knee joint is another common symptom. This occurs as a result of inflammation caused by the injury.
- Stiffness: Individuals with a torn meniscus may experience stiffness in the knee, making it difficult to fully straighten or bend the joint.
- Locking or Catching Sensation: A torn meniscus can cause the knee to catch or lock in a certain position, restricting movement and causing discomfort.
- Instability: Some individuals may feel a sense of instability or weakness in the knee, particularly when bearing weight or during activities that involve twisting motions.
Causes of a Torn Meniscus
Several factors can contribute to the development of a torn meniscus, including:
- Trauma: Direct trauma to the knee joint, such as a sudden twist or impact, can cause the meniscus to tear.
- Degenerative Changes: As individuals age, the meniscus can undergo degenerative changes, making it more susceptible to tears, even with minimal trauma or stress.
- Overuse: Repetitive movements or activities that place excessive stress on the knee joint, such as squatting or lifting heavy objects, can increase the risk of a torn meniscus.
- Sports Injuries: Athletes involved in sports that require sudden changes in direction, pivoting, or jumping are at higher risk of sustaining a torn meniscus. Sports like soccer, basketball, and football are common culprits.
Treatment Options
The appropriate treatment for a torn meniscus depends on various factors, including the severity of the injury, the individual’s age, activity level, and overall health. Treatment options may include:
- Rest and Ice: Resting the knee and applying ice packs can help reduce pain and swelling in the initial stages of the injury.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles surrounding the knee joint and improving flexibility can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further injury.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may help manage pain and inflammation.
- Bracing: Wearing a knee brace or using supportive devices can provide stability and reduce strain on the injured meniscus.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases where conservative measures fail to provide relief, or if the tear is severe, surgical intervention may be necessary. Arthroscopic surgery, a minimally invasive procedure, may be performed to repair or remove the torn portion of the meniscus.
Conclusion
A torn meniscus can significantly impact one’s quality of life, causing pain, swelling, and limited mobility. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of this common knee injury is essential for timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By seeking prompt medical attention and following recommended treatment protocols, individuals can effectively manage a torn meniscus and return to their normal activities with reduced discomfort and improved function.